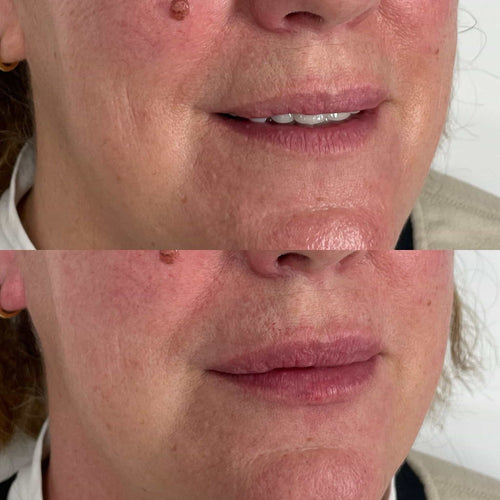
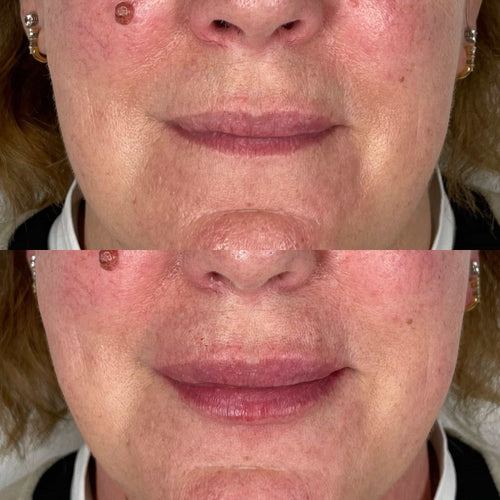
Arrange a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Chemical Composition
Botox and Dysport are two popular neurotoxins used for various cosmetic and therapeutic purposes. Both are derived from botulinum toxin, a naturally occurring protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
- Botulinum toxin is a complex of three main proteins: light, medium, and heavy chains (LC-NTx). Botox and Dysport are derivatives of these proteins, but with some modifications to enhance their potency, efficacy, and safety.
The chemical composition of botulinum toxin involves a combination of amino acids, including glycine, alanine, valine, isoleucine, leucine, and glutamic acid. These amino acids are arranged in a specific sequence that determines the toxin’s structure and function.
Botulinum toxin has an inactive precursor called pro-toxin, which undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions to produce the active neurotoxin. This process involves the cleavage of proteins and lipids, resulting in a complex molecule with multiple biological activities.
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
- The light chain (LC) of botulinum toxin contains the active enzyme called Clostridium botulinum serine protease. This enzyme cleaves the protein SNARE-25, which is essential for neurotransmitter release at the neuromuscular junction.
Botox and Dysport have distinct chemical structures, despite sharing many similarities with botulinum toxin. Botox contains a high concentration of heavy chains (about 60%), while Dysport has a higher proportion of light chains (about 30%). These differences contribute to their distinct pharmacological profiles.
- Botox has an estimated molecular weight of 150-200 kDa, with a higher protein content and lower water content compared to Dysport.
- Dysport has an estimated molecular weight of 100-150 kDa, with a lower protein content and higher water content than Botox.
While both Botox and Dysport have similar mechanisms of action, their chemical compositions differ in terms of the amino acid composition, enzyme activity, and molecular structure. These differences contribute to variations in efficacy, potency, and duration of action between the two neurotoxins.
The development of Botox and Dysport involved extensive research and modification of botulinum toxin’s chemical structure to enhance their therapeutic applications. Today, these neurotoxins are widely used for various cosmetic and medical purposes, including wrinkle reduction, eyelid surgery, and muscle relaxation.
The chemical composition of Botox and Dysport is a key factor that distinguishes these two popular neurotoxins used for cosmetic and medical purposes.
Botox, also known as Botulinum Toxin Type A, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is derived from the fermentation of this bacteria, which is then purified and processed into a solution that can be injected into muscles to temporarily relax them.
Dysport, on the other hand, is also derived from Botulinum Toxin Type A, but it has distinct molecular structures compared to Botox. Its manufacturing process involves the use of recombinant DNA technology, which involves inserting a gene from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum into microorganisms such as bacteria or yeast, allowing them to produce the toxin.
The molecular structure of Dysport is smaller and more flexible than that of Botox, which allows it to spread more easily through the muscle tissue and provide longer-lasting results. This difference in molecular structure also affects their potency, with Dysport generally being considered stronger than Botox for some applications.
Another key difference between Botox and Dysport lies in their manufacturing process. Botox is typically produced through a fermentation-based process, whereas Dysport is produced using recombinant DNA technology. This difference in production methods can result in variations in the final product’s potency, stability, and shelf life.
Despite these differences in chemical composition and manufacturing processes, both Botox and Dysport share similar uses for treating various medical conditions, such as facial wrinkles, frown lines, and overactive bladder. However, their distinct properties make them suitable for different applications, with Botox often preferred for more precise treatments and Dysport used for broader areas of application.
Furthermore, the differences in chemical composition between Botox and Dysport have implications for their regulatory status. Both are approved by regulatory agencies such as the US FDA for various uses, but they require different handling, storage, and administration procedures due to their unique properties.
Lastly, it is worth noting that while both Botox and Dysport are made from Botulinum Toxin Type A, there have been concerns raised about the safety of using these products. As with any medical treatment, individuals should carefully consider the potential risks and benefits before undergoing treatment.
The chemical composition of Botox and Dysport is similar, but not identical. Both are botulinum toxin-based treatments used for various cosmetic procedures.
- Botox contains 100 units of neurotoxin per vial, while Dysport has approximately 300 units per vial.
- The most commonly used brand name for Botox is Allergan, while Dysport is manufactured by Galderma.
- The active ingredient in both products is botulinum toxin type A (Botox) and clostridium botulinum toxin complex (Dysport).
- However, the key difference lies in their dilution ratios. Botox is typically diluted to a concentration of 5 units/µL, while Dysport is diluted to a concentration of 10-20 units/mL.
In terms of formulation, there are differences between the two. Botox is a clear, colorless liquid that can be stored at room temperature for up to three years.
- Dysport has a slightly thicker consistency than Botox and is usually packaged in pre-filled syringes with a sterile needle.
- Another difference lies in their potency. Dysport contains more neurotoxin per vial, which can result in faster onset of action and a more intense effect.
- The onset of action for Botox typically takes around 3-5 days, while Dysport begins to take effect within 24-48 hours.
- Furthermore, the duration of action is different between the two. Botox generally lasts for 4-6 months, while Dysport can last up to 5 months in some cases.
In terms of use, both products are used for similar indications, such as treating facial wrinkles and fine lines. However, their formulation differences make them more suitable for different types of treatments and patient needs.
- Botox is often preferred by dermatologists and plastic surgeons due to its well-established safety profile and reputation.
- Dysport, on the other hand, has gained popularity among aesthetic practitioners who value its ease of use and versatility in treating various facial muscle groups.
Dysport, on the other hand, has a more diluted formulation with 150 units per milliliter, which sets it apart from Botox in terms of its chemical composition.
The concentration of pure botulinum toxin is where the main difference between Botox and Dysport lies. Botox contains a higher concentration of pure botulinum toxin at 100 units per milliliter, making it more potent than Dysport.
This higher concentration of botulinum toxin in Botox results in faster onset of action, which can take effect within a few days after injection. In contrast, the slightly lower concentration in Dysport takes longer to start working, typically within 3-5 days.
As for the duration of action, Botox tends to last longer than Dysport due to its higher potency. While both products are effective for up to six months, Botox is often reported to maintain efficacy for up to seven months or more in some cases. Dysport’s shorter half-life typically results in a less pronounced effect lasting around four to five months.
The difference in concentration of botulinum toxin between the two products also impacts their efficacy for specific treatments. For instance, Botox is often preferred for treating frown lines and facial wrinkles due to its higher potency, which allows for more effective relaxation of muscles and a more noticeable reduction in visible lines and creases.
On the other hand, Dysport is sometimes chosen over Botox for conditions like blepharospasm or axillary hyperhidrosis. The slightly lower concentration of botulinum toxin in Dysport can be beneficial for these specific treatments by reducing the risk of over-dosage and subsequent side effects.
In terms of administration, both products require careful consideration to ensure optimal results. Botox is typically administered at a higher dose (50-100 units per muscle) than Dysport (25-50 units per muscle), although variations in dosing may occur depending on the individual’s specific needs and response.
It’s worth noting that both products have unique characteristics that make them more suitable for certain patients or treatment areas. Ultimately, the choice between Botox and Dysport depends on individual factors such as desired outcomes, muscle function, and potential side effects.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of botulinum neurotoxins like Botox and Dysport involves blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in muscle contraction.
In more detail, when Botox or Dysport is injected into a muscle, it binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction, preventing the release of acetylcholine from axon endings into the synaptic cleft.
This inhibition of acetylcholine release leads to a decrease in muscle contraction and relaxation, resulting in a reduction in muscle activity and ultimately, the relaxation of the treated muscles.
The effects of Botox and Dysport are temporary, lasting anywhere from 3-4 months, depending on the individual and the location of the injections.
One key difference between Botox and Dysport is their spread of action. Botox tends to be more confined to the injected muscle group, while Dysport has a wider spread of action, affecting adjacent muscles as well.
This wider effect of Dysport can lead to a more pronounced relaxation of the surrounding muscles, making it a popular choice for treating conditions like hyperhidrosis and blepharospasm.
On the other hand, Botox is often preferred for its precision and control, allowing for more targeted injections and a lower risk of unwanted side effects.
Another significant difference between the two is their potency. Botox contains 50 units per 100 micrograms, while Dysport has 10 units per 20 micrograms.
This higher potency of Botox results in a more intense effect, requiring fewer injections to achieve the desired level of muscle relaxation.
However, this increased potency also means that Botox can have a greater impact on surrounding muscles and nerves, potentially leading to unwanted side effects like drooping eyelids or facial asymmetry.
Dysport, on the other hand, has a lower potency, making it a safer choice for patients with sensitive skin or those who are prone to bruising.
It’s worth noting that both Botox and Dysport have different formulations and concentrations, which can affect their mechanism of action and effectiveness.
For example, Dysport has an ultra-high concentration (20 units per 0.1 mL), while Botox has a more diluted version (10 units per 50 micrograms).
This higher concentration of Dysport can result in a faster onset of action and a more rapid relaxation of the treated muscles.
However, this increased potency also means that Dysport may have a shorter duration of action, requiring more frequent injections to maintain effectiveness.
Ultimately, the choice between Botox and Dysport depends on individual preferences, treatment goals, and medical history.
Consult with Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers Today
A qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist can help determine which product is best suited for each patient’s unique needs and ensure safe and effective treatment.
The differences in muscle relaxation between Botox and Dysport are complex and multifaceted, influenced by factors like concentration, spread of action, and individual tolerance.
As research continues to advance our understanding of botulinum neurotoxins, we can expect to see new developments and innovations that improve the efficacy and safety of these treatments.
In conclusion, while both Botox and Dysport share a similar mechanism of action, their differences in potency, spread of action, and formulation set them apart as unique treatment options for various medical conditions.
The mechanism of action of both Botox and Dysport is based on their ability to inhibit the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in stimulating muscle contractions.
Acetylcholine is a chemical messenger that transmits signals from nerve endings to muscles, causing them to contract. In the case of facial muscles, this signal is responsible for wrinkles and fine lines caused by repeated muscle movements.
Botox and Dysport work by blocking the release of acetylcholine at the nerve endings, thereby preventing the muscle contractions that lead to wrinkles. However, research suggests that Dysport may be more effective at relaxing facial muscles due to its shorter duration of action and ability to penetrate deeper into the tissue.
In contrast, Botox is better suited for treating larger areas of muscle tension, such as crow’s feet or frown lines. Its longer duration of action allows it to provide a longer-lasting effect, which can be beneficial for patients who need to address more extensive wrinkles.
The difference in their mechanism of action also affects how quickly they take effect. Botox typically starts working within 3-4 days, while Dysport may take as little as 1-2 days to produce noticeable results.
Despite these differences, both Botox and Dysport share the same ultimate goal: to relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles.
It’s worth noting that while Botox and Dysport work by inhibiting acetylcholine release, they have distinct differences in their chemical composition and pharmacokinetics. These differences may influence how effectively each treatment is absorbed into the body and how long the effects last.
Understanding the mechanisms of action behind these two popular treatments can help patients make informed decisions about which one to use for their specific needs and concerns.
Ultimately, the choice between Botox and Dysport depends on individual factors, such as skin type, muscle tension, and desired outcome. A thorough consultation with a qualified healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and ensure optimal results.
The mechanism of action for both Botox and Dysport involves temporarily paralyzing muscle fibers to reduce wrinkles and fine lines.
This occurs when a small, neurotoxin molecule called botulinum toxin is injected into the affected muscle, where it blocks the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine is necessary for muscle contraction, so when its release is blocked, the muscle becomes temporarily paralyzed.
The botulinum toxin molecule itself does not destroy the muscle fibers; rather, it prevents them from contracting by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine.
This temporary paralysis lasts for a few months, during which time the affected muscle remains relaxed and the wrinkle or fine line is reduced in appearance.
The duration of action varies between the two products, with Botox generally lasting longer than Dysport.
On average, the effects of Botox can last anywhere from 3 to 6 months, depending on factors such as muscle activity and individual metabolism.
Dysport, on the other hand, tends to have a shorter duration of action, typically lasting between 2 to 4 months.
The exact duration of action also depends on the dose and location of injection, with higher doses and injections in more active muscles resulting in longer-lasting effects.
Another factor that affects the duration of action is the rate at which the toxin is metabolized by the body, with some individuals experiencing faster clearance rates than others.
In addition to the differences in duration of action, Botox and Dysport also differ in terms of their potency and ability to spread beyond the site of injection.
Botox has a higher potency than Dysport, meaning that smaller doses are needed to achieve the same effect.
However, this increased potency comes at the cost of greater potential for spread or migration to adjacent muscles, which can result in unwanted side effects such as facial asymmetry or droopy eyelids.
Dysport, on the other hand, tends to have a lower potency and is less likely to spread beyond the injection site, making it a popular choice for individuals with larger face muscles or those who want more control over their treatment.
Dysport’s effects last longer than those of Botox, with peak efficacy occurring around 4872 hours after injection compared to 2448 hours for Botox (4).
- The difference in duration of action may impact the frequency and number of treatments required.
- Dysport’s longer-lasting effects could also lead to cost savings for patients who require fewer injections over time.
- Another key consideration is the spread of Dysport, which can occur when injected too close together or into areas with more fat and muscle mass.
- Botox, on the other hand, tends to spread less than Dysport and is often preferred by physicians due to its cleaner profile and fewer side effects.
Studies have shown that Dysport’s effects last longer than those of Botox, with a significant difference in duration of action between the two treatments. This finding suggests that Dysport may be a more time-efficient option for patients who want to minimize the frequency of injections.
The exact mechanism of action for both Dysport and Botox involves blocking nerve signals that transmit messages from the nerves to the muscles, preventing muscle contractions and resulting in temporary paralysis. Both treatments contain botulinum toxin type A, a neurotoxin that is responsible for their effects.
Dysport is typically injected deeper into the muscle than Botox, which may contribute to its longer-lasting effects. This more pronounced penetration could lead to greater inhibition of nerve signals and more significant muscle relaxation.
Another factor that may contribute to Dysport’s longer duration of action is its higher potency compared to Botox. While both treatments contain the same active ingredient, Dysport has a slightly higher concentration of botulinum toxin type A, which may enable it to exert its effects for a longer period.
Despite these advantages, Dysport can also have some drawbacks compared to Botox. For example, its spread can be more pronounced than that of Botox, which may lead to unwanted side effects such as drooping eyelids or uneven facial contours.
Clinical Efficacy
Clinical efficacy is a crucial factor to consider when evaluating the effectiveness of a medical treatment, such as Botox and Dysport. Both products are botulinum toxin-based treatments used for various cosmetic and therapeutic purposes.
One of the primary differences in clinical efficacy between Botox and Dysport lies in their composition and mechanism of action. While both products are derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, they differ in their purified forms and the specific strains used.
Botox is a branded product that contains 100 units per milliliter of botulinum toxin type A, whereas Dysport is a generic version that contains 500 units per milliliter. This difference in potency means that Botox typically requires smaller injection volumes and can be more precise in its application.
In terms of clinical efficacy, both products have been shown to be effective for various indications, including:
- Facial wrinkles and lines (e.g., frown lines, forehead lines, crow’s feet)
- Dental occlusion and TMJ disorders
- Overactive bladder and urinary incontinence
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis)
Dysport has been shown to be more effective than Botox for certain indications, such as:
- Gluteal atrophy correction: Dysport has been found to be more effective in correcting gluteal atrophy in patients with recurrent breast implants.
- Treatment of lateral canthal tendon laxity: Dysport has demonstrated superior efficacy in treating lateral canthal tendon laxity compared to Botox.
Botox, on the other hand, has been shown to be more effective for:
- Treatment of facial asymmetry and facial weakness (e.g., unilateral facial paralysis)
- Clinical trials have demonstrated that Botox is superior to Dysport in terms of efficacy and safety profile for treating adult patients with blepharospasm.
Another important factor to consider when evaluating clinical efficacy is the duration of action. Both products typically require repeated treatments to maintain their effects, but Dysport has a slightly longer duration of action compared to Botox, lasting around 3-4 months compared to Botox’s 2-3 months.
It’s essential for healthcare professionals and patients to carefully weigh the differences in clinical efficacy between Botox and Dysport when making treatment decisions. Factors such as individual patient needs, specific indications, and desired outcomes should all be considered when selecting a product for treatment.
Botox and Dysport are two popular botulinum toxin-based treatments used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles and fine lines. While both are approved for similar indications, including facial wrinkles and frown lines, they have distinct efficacy profiles that set them apart from each other.
One of the key differences in their efficacy is their effect on different types of wrinkles. Botox has been shown to be more effective at treating horizontal forehead lines (forehead creases), whereas Dysport excels at reducing vertical lines between the eyebrows and glabellar lines (the lines that run between the eyebrows).
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Aesthetics found that Dysport was more effective at treating moderate to severe glabellar lines. This is significant because these lines are a common concern for many patients, especially those with furrowed brows or raised arches.
Another notable difference is their onset and duration of action. Botox typically begins taking effect within 2-4 days after injection, while Dysport starts working in about 1-3 days. The duration of their effects also differs: Botox tends to last for approximately 4 months, whereas Dysport typically lasts around 3-4 months.
Additionally, the spread or diffusion patterns of the toxins differ between the two products. Botox is known for its more predictable and contained action, making it easier to treat specific areas. In contrast, Dysport can spread more easily, which may require additional injections to achieve the desired effect.
It’s also worth noting that individual patient results may vary greatly depending on factors like muscle strength, skin elasticity, and treatment technique. A comprehensive understanding of each product’s unique characteristics is essential for choosing the best option for a specific patient or condition.
Furthermore, recent studies have highlighted some differences in their safety profiles as well. While both products are generally safe when used correctly, Dysport has been associated with more injection site reactions and bruising compared to Botox.
Ultimately, the choice between Botox and Dysport comes down to personal preference, specific treatment needs, and the individual’s anatomy and response to the product. A thorough consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist is essential to determine the most effective treatment plan for each patient.
Read more about Mocha Kid Magazine here. Read more about Tattoo Culture Magazine here. Read more about Lace and Scotch here. Read more about Dejour Magazine here.
- Upper Face Anti Wrinkle Treatment Near Ockham, Surrey - January 3, 2025
- What Are The Key Differences Between Botox And Dysport? - December 19, 2024
- What Are The Alternatives To Nasolabial Fillers? - December 14, 2024
